Panelized vs. Mobile Homes: Exploring the Differences


When choosing a place to call home, numerous options are available, each catering to different needs and preferences. Panelized and mobile homes offer unique benefits requiring careful consideration to understand their differences.

Customer built Cottage model on a Tennessee farm.
Panelized homes made with structural insulated panels (SIPs) represent a modern approach to traditional housing construction. In contrast, mobile homes are a more budget-friendly housing alternative known for their mobility, and commonly known as "trailer” homes.
This overview helps you to understand the differences between these two types of prefabricated housing, including their construction methods, energy efficiency, and design flexibility. With this information, prospective builders can make an informed decision about which housing option may be best for building a new home.
What to Know about Building with Structural Panels
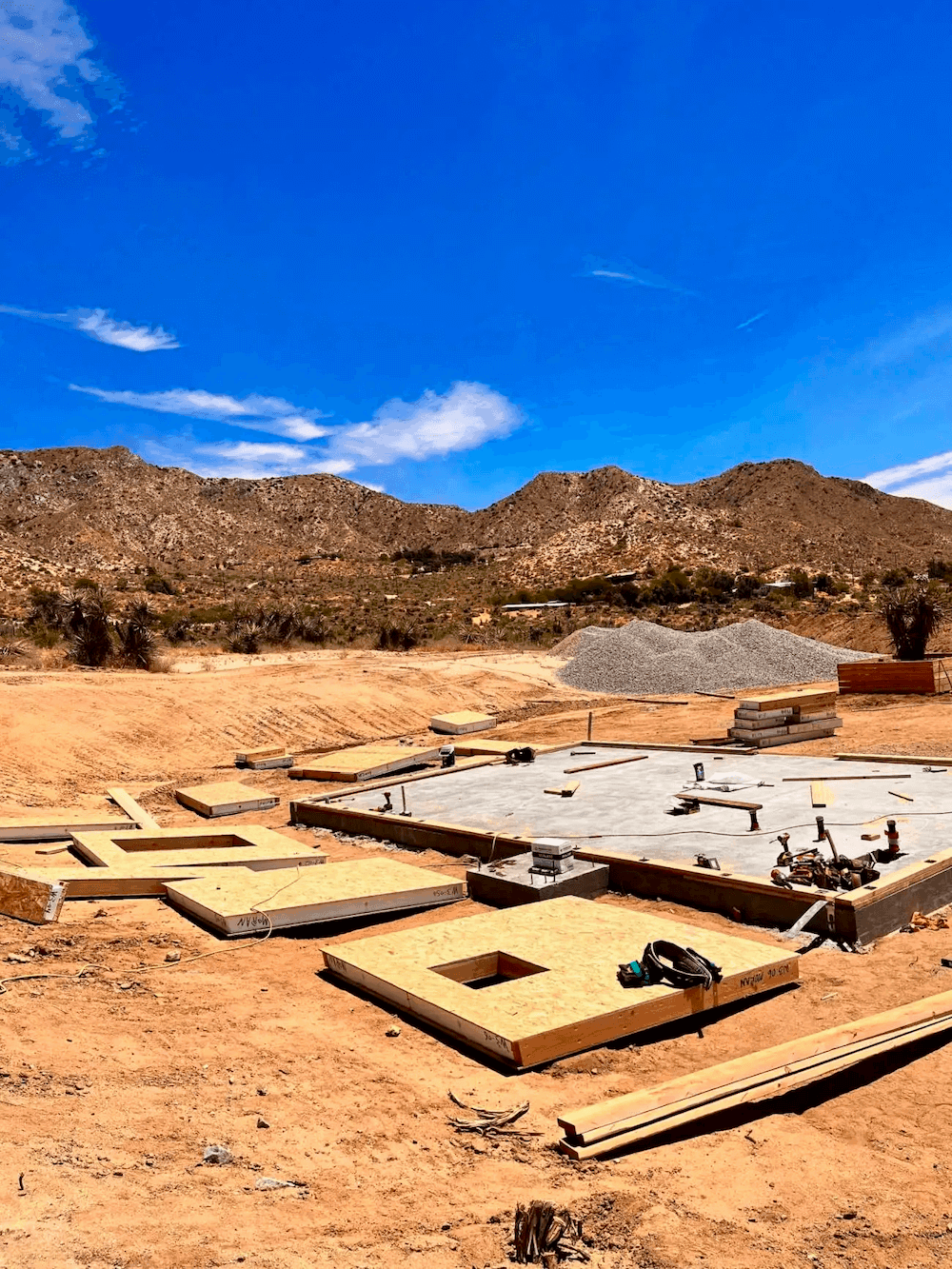
Panels were positioned around a foundation at this California desert location. Mighty Small Homes panels meet strict requirements in the state.
SIP home panels are precision-engineered and cut in a factory, ensuring consistent quality that minimizes waste, especially at the construction site.
SIPs consist of an insulating foam core sandwiched between two structural panels. This assembly creates a robust and exceptionally well-insulated shell for your home that also boasts the strength of a steel i-beam structure.
Since 2007, SIP walls gained recognition in the International Residential Code, showing they're as good as other approved building methods.
The regulations and standards in the IRC govern the construction of residential buildings. It includes guidelines for building design, materials, safety, and construction methods to ensure safe and habitable homes.
Being included in these standards makes it easier for builders and designers using SIP walls in homes to follow the rules without extra technical work.
Here's a brief overview of what you need to consider.
Important Differences Between Panelized and Mobile Homes
| Criteria | SIP Homes |
Mobile Homes |
|---|---|---|
Building Materials |
Panelized homes utilize SIPs, which offer superior insulation, durability, and energy efficiency | Mobile homes use metal frames, wood, fiber cement which are less efficient than a SIP |
Construction Process |
Precisely engineered in factories, assembled on-site | Constructed in factories, transported and set or assembled on-site |
Design Flexibility |
Highly flexible, open floor-plan configurations | Limited customization due to transportability constraints |
Energy Efficiency |
Excellent insulation, energy-efficient | Varies; newer models designed with improved insulation |
Strength |
Exceptionally strong, engineered structures | Must meet specific standards but generally have less structural integrity |
Construction Time |
Quick assembly, reduces building time | Faster construction compared to traditional homes |
Foundations |
Various foundation options, adaptable | Anchored to foundation systems, often concrete piers or slabs |
Cost |
Moderate to high initial cost, potential long-term savings due to energy efficiency | Generally lower initial cost, but long-term costs vary |
Resale Value |
Typically maintains good resale value | Resale value can vary based on age, condition, and location |
Equity |
Can appreciate in value with improvements | May appreciate as much as traditional homes. Classification as personal property affects value. |
Operating Costs |
Lower operating costs due to energy efficiency | Varies based on insulation and energy efficiency |
Design Flexibility |
Highly versatile, accommodating various architectural styles | Limited customization due to transport constraints |
SIPs Meet Modern Standards and Best Practices
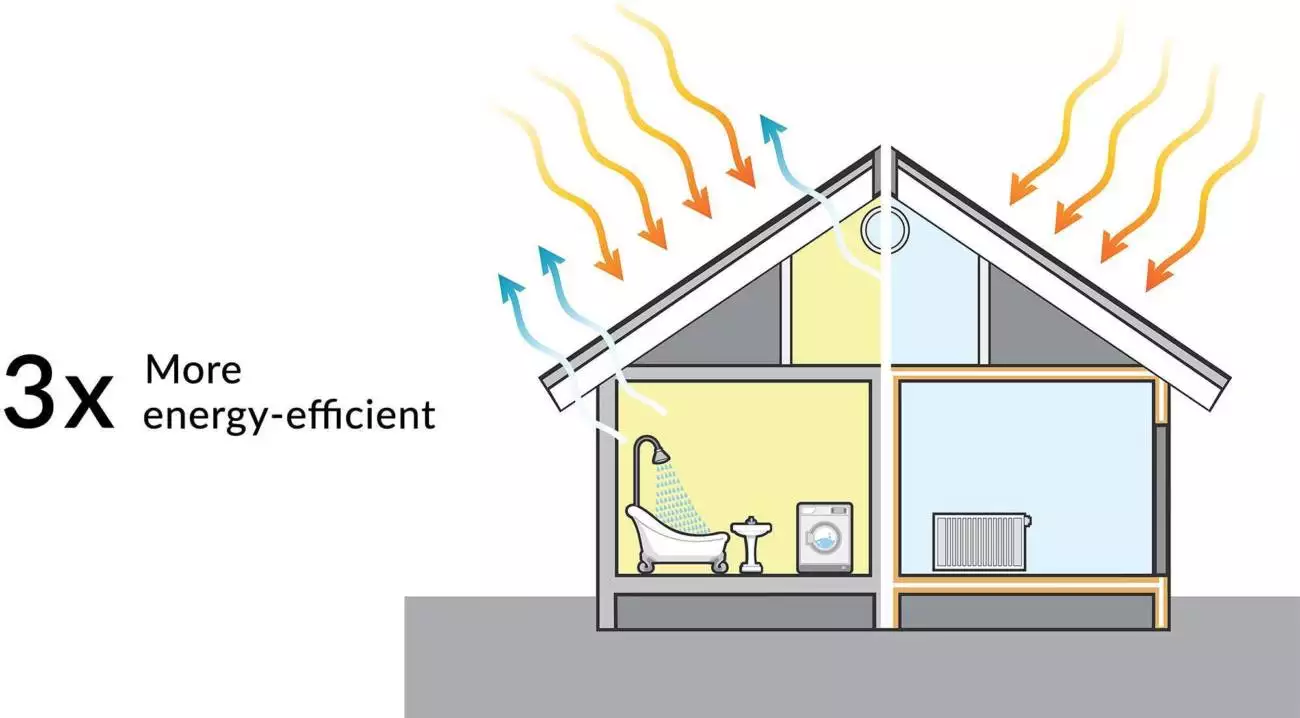
Structural Insulated Panels used for Mighty Small Homes kits offer 3x the energy efficiency of traditional homes.
Structural Codes: SIPs are engineered structures and must meet the standards outlined in building codes. Local engineers often evaluate SIP designs to ensure compliance with local regulations.
Energy Efficiency Standards: SIPs are renowned for their excellent insulation properties, contributing to energy efficiency. They often meet or exceed energy efficiency standards set by organizations like the U.S. Department of Energy.
Fire Safety: SIPs are generally safe in fires due to their fire-resistant properties, but local codes may specify additional requirements, such as fire-resistant coatings or sprinkler systems.
Zoning Regulations: Zoning regulations can impact the placement and design of homes. Understanding local zoning laws is essential to determine the permissible land use and setbacks for constructing panelized homes.
Foundation Codes: Homes must comply with foundation codes, ensuring the foundation's stability and safety. This includes factors like load-bearing capacity and soil analysis.
Electrical and Plumbing Codes: Panelized homes must adhere to electrical and plumbing codes, ensuring the safety and functionality of the home's systems.
The Benefits of Homes Built Using Prefabricated Panels
SIP houses are not just different from traditional stick frame homes–they offer unique benefits and advantages for homeowners before, during, and after the construction is completed.
Insulation and Structural Integrity
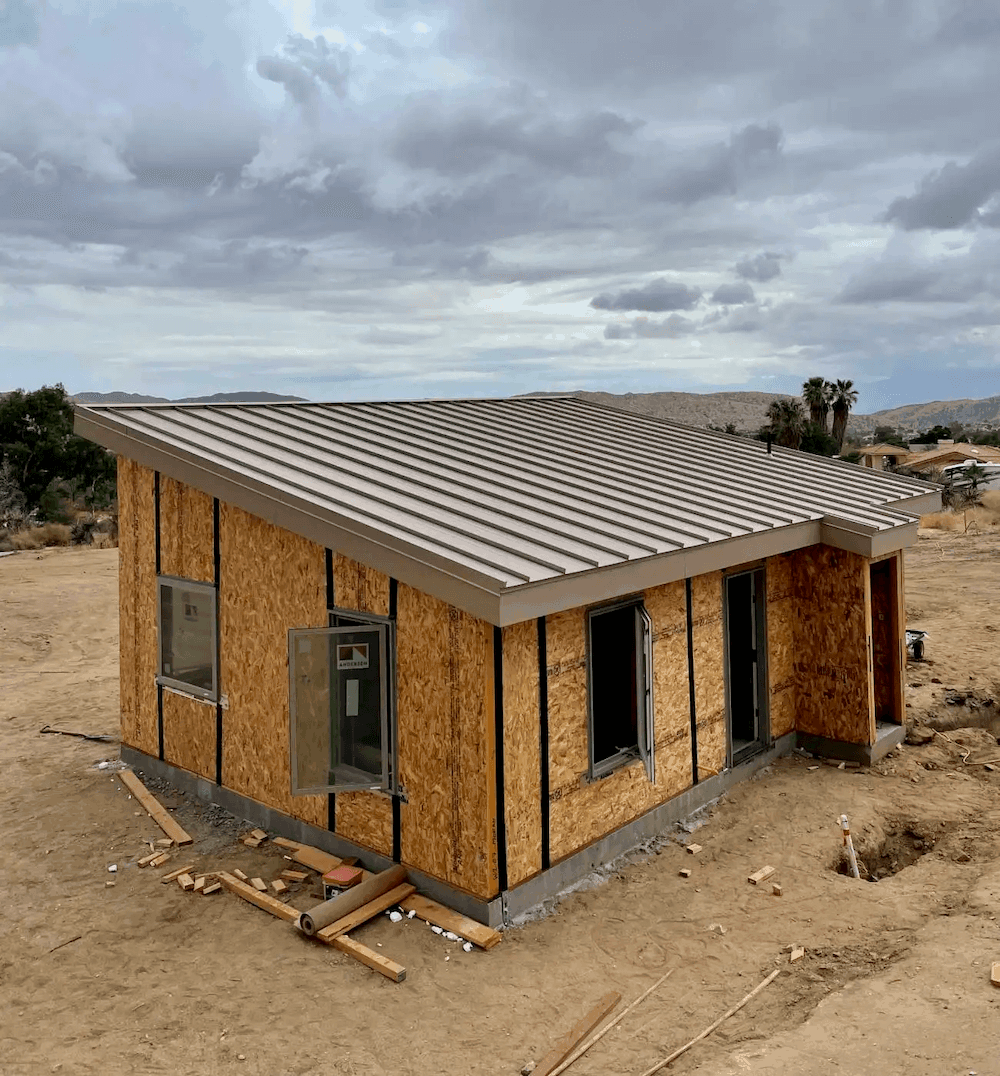

A panel home can be under roof in a couple of days. Following that, windows, doors, roofing, and siding can begin.
Structural insulated panels consist of an insulating foam core sandwiched between two structural panels. This assembly creates a robust and exceptionally well-insulated shell for your home. In fact, a properly-engineered SIP creates structural strength that is equivalent to a steel I-beam.
Also keep in mind that SIPs are precision-engineered in a factory, which ensures consistency and quality that minimizes waste, especially at the construction site.
Financing and Selling
Compared to mobile homes, panelized prefab houses are much easier to finance with a mortgage loan secured by the government. Mobile homes will often not qualify for these mortgages, so you may end up paying higher interest rates or closing costs on the loan. If the owner of a panelized home decides to sell the home in the future, its resale value will be much higher than that of a mobile or trailer home.
Shortened Construction Time
Panels streamline construction, reducing building time and labor costs compared with traditional building methods. Compared to a traditional stick-built home, your SIP home can be under roof in a couple of days and completed in about a third of the time.
Design Flexibility
Panelized homes offer an exciting degree of design flexibility. The interior space of a SIP home is often completely open, offering a range of floor-plan configurations.
The versatility of SIPs allows for builders to choose from a wide range of architectural styles and customization options, whether in a modern contemporary, a traditional ranch, or a classic cottage style.
Popular SIP House Kit Designs
Foundational Stability
The strength of a home starts from the ground up, and SIPs offer advantages since they are particularly strong. Homes built using SIPs can be constructed on various foundations, including concrete slabs, crawl spaces, and basements. The load distribution of SIPs allows for flexibility in foundation design, accommodating different soil types and site conditions. This versatility ensures stability and durability, regardless of the foundation choice.
Severe Weather Resilience
Once constructed, SIP panels create resilient housing structures that are capable of withstanding severe weather events such as tornadoes and hurricanes. SIPs resist winds up to 150 mph and offer greater protection from wind-blown debris.
Energy Efficiency
SIPs are renowned for their outstanding thermal insulation properties. The foam core within the panel significantly reduces heat transfer, ensuring superior energy efficiency. This high insulation factor substantially reduces heating and cooling demands, lowering homeowners' energy consumption and utility bills. SIPs homes maintain a consistent and comfortable indoor temperature year-round, enhancing the overall living experience.
The inherent design of SIPs, with their solid insulation core and minimal thermal bridging, provides a more efficient thermal envelope.
Mobile Homes and Trailer Homes

Trailer homes must meet federal standards.
Within the housing market, mobile homes are often called a "home on wheels" but to be clear, they are not the same as "motor homes", a term most often used to reference RVs (recreational vehicles), including fifth-wheel RVs towed with a pickup truck.
Building Codes for Mobile Homes
Building codes and standards for mobile homes are specific and essential to ensure the safety and structural integrity of these homes, which are designed to be movable.
In the United States, mobile homes are regulated by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). The agency sets comprehensive construction and safety standards for all mobile homes. These standards cover various aspects, including structural integrity, energy efficiency, plumbing, heating, and electrical systems.
Wind and Snow Loads: Mobile homes must be designed to withstand specific wind and snow loads, ensuring they can withstand adverse weather conditions. These requirements vary based on the geographic location where the mobile home will be placed.
Foundation and Anchoring: Mobile homes must be securely anchored to a foundation system, including concrete piers or slabs, to prevent movement during high winds or other environmental factors. Proper anchoring is crucial for the stability and safety of the home.
Transportation Standards: Mobile homes must meet transportation standards if they need to be relocated. This includes securely fastening the home to the semi-trailer and meeting road safety regulations, including size and weight limits.
Electrical and Plumbing Systems: Mobile homes must comply with specific electrical and plumbing codes. These codes ensure the safe installation and operation of systems within the home, considering the unique challenges of mobile structures.
Fire Safety: Mobile homes must have smoke detectors and, in some cases, fire sprinkler systems to enhance fire safety measures. Proper ventilation and fire-resistant materials are also important aspects of the construction standards.
Site Preparation: The site where a mobile home is placed must be properly prepared to ensure drainage, stability, and safety. This preparation often includes grading the land, creating a stable base, and assuring proper drainage away from the home.
Compliance with these building codes and standards is essential for the safety and well-being of mobile home occupants. Additionally, regulations may vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, so it's crucial to consult local authorities or housing agencies to ensure full compliance with all applicable standards and codes.
Considerations For Choosing a Mobile Home

Completed mobile homes must have ample space for delivery to a lot.
A mobile home can provide comfortable living spaces despite limitations. Anchoring the home securely to a foundation system is crucial for stability and safety, while energy efficiency varies based on factors like age and insulation quality, prompting consideration of potential upgrades.
Construction and Mobility
Mobile homes are constructed entirely in a factory and transported to their final location. In the case of a single-wide trailer, it is transported to the lot and can be moved in the future. In the case of “double-wide” mobile homes, two halves are manufactured in the factory and then joined at the home’s location.
While mobility offers a limited advantage, it also comes with trade-offs. Mobile homes, often called “trailer homes,” may have limited design options compared to traditional homes. Mobile homes are only suitable for some locations.
Limited Design Options
Mobile homes are known for their limited customization options compared to traditional homes. This limitation arises from the need for transportability, which necessitates adherence to specific size and weight constraints. This doesn’t mean that mobile homes lack charm or comfort. Many mobile homes are well-designed and can provide cozy living spaces, although homeowners may need to work within certain constraints when personalizing their space.
Foundation Considerations
The foundation of a mobile home is a critical aspect of its strength and stability. They are much more susceptible to wind damage even when anchored to a foundation system Proper anchoring prevents movement during less extreme wind or other environmental factors. Site preparation, including land grading and adequate drainage, is essential to maintain stability and safety.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency in mobile homes can vary widely depending on several factors, including the house’s age and insulation quality. While some older mobile homes may be less efficient, newer models are designed with improved insulation and energy-saving features. When considering a mobile home, it’s essential to inquire about its energy efficiency features and potential upgrades.
Double Wide Mobile Home

“Double-wide” mobile homes combine two single-wide trailer homes into one.
The term “double wide” mobile home signifies a prefab home with twice the floor space because it is constructed out of two sections or halves, unlike single-section mobile homes which are transported in one piece.
Double-wide homes are manufactured in two separate sections, then transported to the site and joined. With various floor plans and layouts, this concept offers more design options.
SIP vs. Mobile Homes: Pros and Cons
We've summarized a lot of the information above into a few simple pros and cons that may help you decide whether to build a home structural insulated panels instead of buying a mobile home.
| Panelized Homes (SIPs) | Mobile Homes |
|---|---|
| Pros | |
| Superior insulation and durability | Affordable initial cost |
| Extensive customization options | Mobility options, allowing for a change of location |
| Potential energy savings and lower utility bills | Quicker construction time compared to traditional stick-built homes |
| Higher resale value, which can be a good investment | |
| Cons | |
| Higher upfront costs | Limited design options due to transportability constraints |
| Longer construction time | Limitations on customization |
| Lower energy efficiency | |
| Higher maintenance costs in the long run | |
Important Considerations for Choosing Your New Housing
To make an informed decision, prospective homebuyers should consider the following factors before moving forward with the purchase of either a panelized or mobile home.
Budget and Financial Factors
Start by assessing your budget comprehensively. Consider not only the initial purchase cost but also the long-term operating expenses. While mobile homes often have a lower upfront cost, panelized homes offer potential savings over time due to their energy efficiency and durability.
Lifestyle and Mobility Requirements
Think about your lifestyle and how it may evolve in the coming years. If mobility is a top priority, mobile homes provide the flexibility to relocate. However, a panelized home may be the better choice if you desire a stable, customized living space.
Consider your long-term plans and whether they involve settling down or exploring new horizons, then select the housing option that accommodates your needs. The reality is that most homeowners do not relocate a mobile home after it arrives and is placed on-site.
Accessibility and Universal Design
The rising demand for accessible housing, related to factors like an aging population and increased awareness about disabilities, emphasizes the importance of incorporating features that enhance usability and livability for everyone. The flexibility of floor plans with panelized homes makes it simpler to incorporate universal design elements like wheelchair-accessible doorways simple.
Building an accessible home is a way of future-proofing when downsizing and can make the more attractive when selling the property.
Safety in a Resilient Home
Having a climate-resilient home becomes a major consideration as weather becomes more severe. Choosing the right type of home becomes a major consideration. As weather undergoes dramatic shifts and the frequency of extreme weather events rises, the demand for resilient home construction has become imperative. The alarming surge in damaging and deadly events such as heat waves, snowstorms, wildfires, floods, hurricanes, and tornadoes poses significant threats, escalating both property damage and human vulnerability.
Mobile homes and even traditional stick-built homes run a higher risk of succumbing to these extreme elements. Panelized homes offer greater resilience and security in a time of uncertainty surrounding future climate challenges.
Aesthetic and Design Preferences

Homes built with SIPs require fewer load-bearing walls, which offer more floor-plan options. Most models offer options for loft space for a den, bathroom, office, or bedroom.
Your ideal living space should align with your aesthetic and design preferences. Consider the architectural style you desire and how much customization you crave. Panelized homes offer many model styles and customization options, allowing you to create a space that perfectly suits your tastes. Mobile homes all look the same. While often well-designed, these homes have design limitations.
Assessing Your Individual Needs for a Home
Ultimately, deciding between panelized and mobile homes will hinge on your unique goals and circumstances. It's crucial to thoroughly explore both options, including visiting model homes and consulting experts if needed, to ensure your decision aligns with your needs and vision for your new home.
When considering your needs, consider your budget, lifestyle, mobility requirements, and design preferences. Each of these plays a vital role in determining which housing solution is the right fit for you.
Seeking Expert Guidance
Making the right housing decision is an important step in securing your future, comfort, and happiness. Seek expert guidance. Reputable home builders, like Mighty Small Homes, take the time to help individuals navigate housing decisions.
Our experienced professionals provide you with personalized advice, answer your questions, and offer insights into the intricacies of panelized and mobile homes. Contact our helpful experts to get started today.
FAQs
Panelized homes comprise structural insulated panels and stick-built panels, each manufactured off site. Both types of panels are assembled on site. Mobile homes, on the other hand, are factory-built and designed to be transportable, often called "trailer homes."
Panelized homes using SIPs offer strength with wind resistance up to 150 mph, superior insulation, extensive customization options, potential energy savings, and a high resale value. They are known for their durability and structural integrity.
Mobile homes are factory-built for consistency, and have quick construction times. They offer some mobility options and are more affordable.
SIP homes with solid foam insulation and air-tight panels, provide excellent efficiency and can be up to 50% more energy-efficient than mobile homes or stick-built homes, resulting in lower utility bills.
The energy efficiency of mobile homes varies depending on factors such as insulation and the age of the home. Newer models are designed with improved insulation, but older ones may be less efficient.
Yes, there are energy efficiency standards for new mobile homes in the United States. These standards are regulated by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). The agency sets specific energy efficiency requirements that manufactured homes must meet. These standards cover various aspects of the home, including insulation, windows, heating systems, and overall energy performance.
Panelized homes generally have higher upfront costs due to their construction methods and materials. Mobile homes are often more affordable initially and have a shorter lifespan compared to panelized homes. With regular maintenance and updates, mobile homes can remain comfortable and functional for many years.
Yes, panelized homes offer extensive customization options and greater design flexibility than mobile homes.
Yes, one of the primary advantages of mobile homes is their mobility. They may be transported to new locations, making them ideal for those who want to change location.
Yes, many mobile homes, especially double-wide models, can be permanently placed on a foundation to provide stability and permanence. However, the process and requirements for converting a mobile home into a permanent structure can vary by location and local regulations.
When buying a mobile home, consider the location of the mobile home park or site, the age and condition of the home, and the quality of insulation and energy-efficient features to ensure it meets your needs and budget.